As record heat waves arrive this summer, it’s essential that your AC unit is properly cooling your home. There could be a number of reasons why your AC is suddenly not cooling. Read on to discover the top reasons that impact AC cooling and where to find a quick turnaround for Denver air conditioner repair.
Top 5 AC Cooling Issues
The air filter needs to be cleaned or replaced. A dirty air filter is one of the biggest reasons why your AC unit might suddenly stop cooling. Air filters help keep dust, dirt, and other debris from entering into the system. When they get too clogged, however, this blocks the pathway of air inside the ducts. AC air filters should be cleaned regularly in order to keep your unit working at full capacity.
You need to adjust the settings. Sometimes AC unit fans can blow warmer air if they are programmed on the wrong settings. Try setting your window AC unit to “AUTO” mode so that the fan only turns on to pump cool air. You can also contact your local Denver air conditioner professional to ensure your home AC unit is on the right setting for your home size.
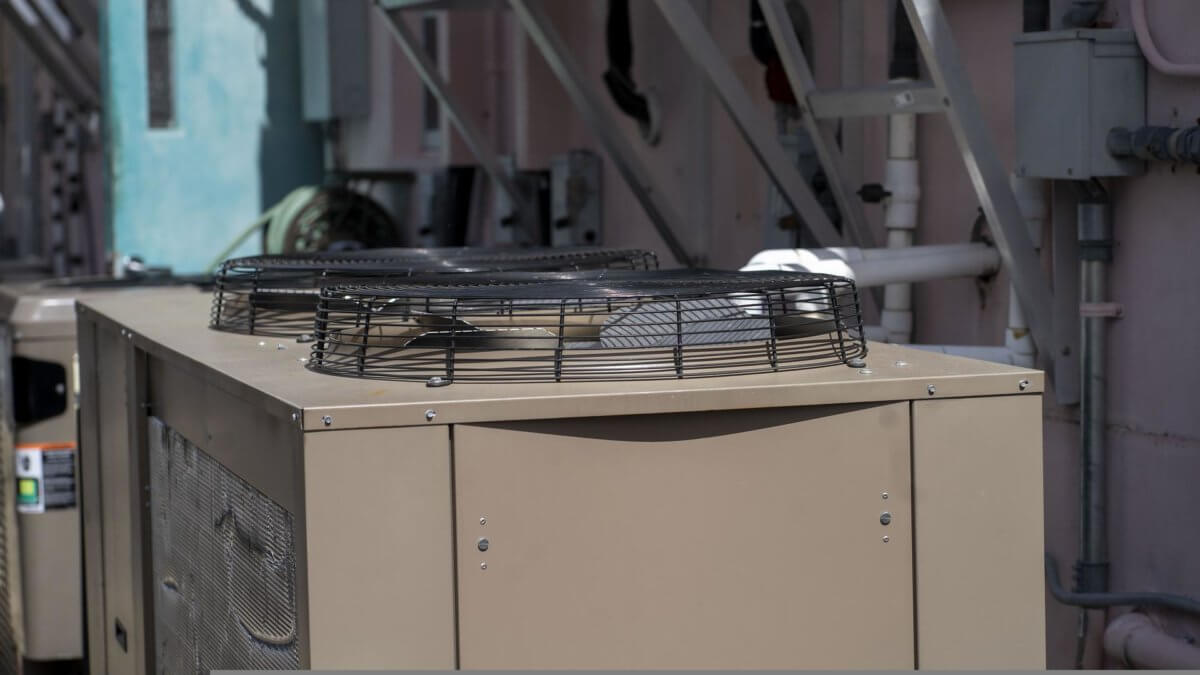
The outside unit is blocked with debris. AC units located outside the home can often stop cooling correctly if blocked or damaged by tree branches, leaves, or other debris. Be sure that the AC condenser is not clogged, as this can impact how the unit transforms hot air into cool air for your home. Getting your outside AC unit maintenanced regularly ensures that it’s always cooling properly.
There is an issue with the motor. Although older units are more susceptible to motor breakdowns, newer units can also experience sudden issues due to extreme temperatures. A faulty or broken motor fan will cause the unit to either blow out hot air – or stop working altogether. Fixing an AC motor is best left to a professional, however. Contact a Denver heating and cooling company for guidance on this issue.
The refrigerant fluid is leaking. AC refrigerant helps absorb heat and turn it into the cool air that pumps into your home. A lack of this fluid is a sure sign that your AC unit will suddenly stop cooling. Check around the unit for leaking refrigerant, a buildup of ice around the unit may be present. Be sure to listen for uncommon noises like hissing or gurgling.
Finding AC repair in Denver
If you’ve checked all of these issues and you are unsure what next steps to take to fix your air conditioning unit, consider the help of a professional. Having a functioning AC unit in extreme temperatures is important for keeping cool and comfortable. Professional technicians at Go Green Heating and Air Conditioning can help fix your AC right away when it stops cooling.
Contact us today for more information on how we can help with AC maintenance and repair.